Looking up Data
Overview
Lists of choices and reference data can be obtained from sources outside of the survey template. This allows you to:
Update the survey with new choices or reference values without changing the survey template.
Share the same data between multiple surveys, for example lists of provinces and districts for a user to select.
Use much larger numbers of potential choices and reference values than you could put directly into a survey without making it too slow to load.
Choices populate select lists; reference data fills calculate values using pulldata().
Sources
Data can be sourced from:
Reference files (CSV or XLSX)
Surveys
Reference files can be CSV or XLSX. Use them for data that does not change too often as it is a manual process to upload an updated file onto the server. Data sourced from other surveys will be available automatically as soon as the data is submitted to the source survey.
Use reference files for stable lists. Use another survey when the reference data needs to update as soon as submissions arrive.
In the remainder of this document the source of the data will be written as SOURCE. Replace this with the name of the reference file or the identifier of the survey that contains your data.
Using Reference Files
Creating the file
The first row of the reference file contains the header. Use the same rules for specifying column headers as are used for question names, that is English characters and underscores with no spaces.
Subsequent rows contain the data. These can contain any characters supported by your phones using Unicode.
Warning
The name of the reference file should not have any spaces.
Loading a reference file onto the server
If your reference file might be used by more than one survey then you should load it onto the server as a shared resource.
Select the Admin module
Select Shared Resources
Click Add File and select the reference files you want to load
Click Upload
Your reference file is now available to any survey that refers to it.
If you want your reference file to be only used by a single survey then:
Select the Admin module
Select Forms
Click the form name to edit it
Select File and then Media
Click Add File and select the reference files you want to load
Click Upload
Referring to the file
Replace SOURCE with the name of the file without the extension. In the following examples the full file name is "locations.csv":
search('locations')
search('locations', 'matches', 'region_v', ${region})
Using another Survey as the Source
Replace SOURCE with "linked_" followed by the ident of the survey. In the following examples the survey ident is s3_23:
search('linked_s3_23')
search('linked_self')
search('linked_s3_23', 'matches', 'region_v', ${region})
Use linked_self to look up data previously submitted in the same survey.
The online editor will guide you through accessing another survey's data. For example to look up choices in another survey select Appearance, click Edit, and then select the Search tab. You can then look up available surveys without having to know their ident.
If you are editing your survey in a spreadsheet then you can find the ident of the survey that you are looking up by using the online editor. Open the survey you want to reference and then select File and then Info.
Warning
The survey that is referenced will need to be in the same organisation as the survey doing the referencing.
Looking up Choices
The approach is similar to using choices from the choices sheet but with the difference that the choices list contains the names of the columns that have the choices rather than the choices themselves. You will also need to add a search() function to the question's appearance telling it where to get the data.
Specifying Column Names
In the name column of the choices list specify the column name that contains the value of the choice.
In the label column(s) of the choices list specify the column name that contains the label for the choice.
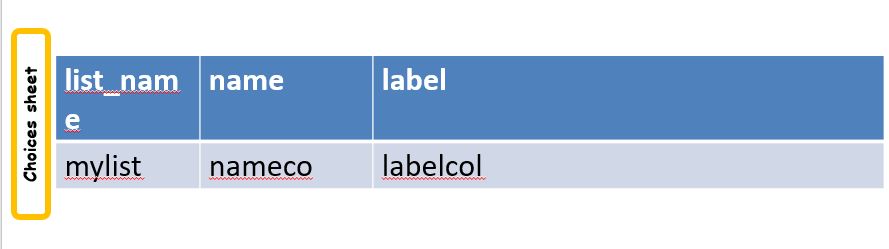
Setting the choice list values
Notes:
In the label you can specify multiple column names separated by commas. The data from each of these columns will then be combined and shown to the user
The value column and the label column can be the same
The choice labels can be in multiple languages as you can specify a different column for each language just as you would normally specify different text for each language
Adding fixed choices
You can add fixed choices to the choices that are sourced from the reference file or survey. For example you may have a select question to look up geographic locations from a survey. These locations may be where your team is working and be maintained in a separate survey. That survey is presumably not going to have a value for a location of "none of these". Hence you can add that directly as a fixed choice. The value must be numeric to distinguish this choice from the choice that identifies in the reference file.
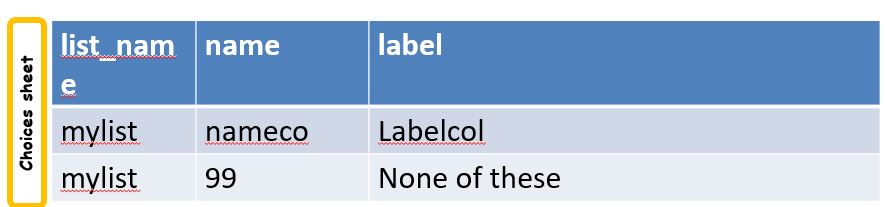
Adding fixed choices
The Search Function
The search function is placed in the appearance of the select question and tells the system where the source of data can be found. This function has between 1 and 5 parameters depending on how complex your filtering requirements are.
search() returns rows used to build the choice list.
Simple (1 parameter)
search('SOURCE')
Looks in SOURCE for the data.
Only this simple form of the search function can be used with WebForms.
Note
Duplicates will be removed.
Filter the data (4 parameters)
search('SOURCE', 'A FILTER FUNCTION', 'COLUMN IN SOURCE TO FILTER ON', FILTER VALUE)
The filter function can be one of:
contains (For use in WebForms requires SmapServer 21.08)
startswith (For use in WebForms requires SmapServer 21.08)
endswith (For use in WebForms requires SmapServer 21.08)
matches
in
not in
eval (Requires FieldTask 6.505 and SmapServer 21.09; not available in WebForms)
The filter values for "in" and "not in" should be lists separated by spaces. Use it with filter values that come from select multiple questions.
Warning
Using column names in the reference file of "name" or "label" to filter on will cause problems in WebForms if these are not also the columns that are used for the value and label of the choice. In other words if you are going to call a CSV column "label" then make sure it does contain the label!
Double filter the data (6 parameters)
Like the normal filter but with an extra "matches".
search('SOURCE', 'A FILTER FUNCTION', 'COLUMN IN SOURCE TO FILTER ON', FILTER VALUE, 'COLUMN TO MATCH ON', VALUE TO MATCH)
Example:
search('children', 'matches', 'class_v', 'class1', 'enrolled_v', 'yes')
Returns all records in the children reference file where the "class_v" column has the value "class1" and the "enrolled_v" column has the value "yes".
Examples
Filter |
Appearance |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
matches |
search('locations', 'matches', 'region_v', ${region} |
Searches locations file for all rows where the region_v column is the same is the answer to the "region" question |
in |
search('product', 'in', 'product_category', ${product_category}) |
Returns all products whose category is in the list of product categories that are selected in the "product_category" select multiple question. |
eval |
search('product', 'eval', "cast(#{age} as integer) > ${min_age} and cast(#{age} as integer) < ${max_age}", 'eval') |
Return all people whose age is between the values selected in the min_age and max_age questions. Note #{name} refers to a column in the data that you are looking up. The 4th parameter is ignored for an eval filter so I just set it to 'eval' again in this example. |
eval and matches |
search('product', 'eval', "cast(#{age} as integer) > ${min_age} and cast(#{age} as integer) < ${max_age}", 'eval', 'region', ${region}) |
As for the eval example above but this time only return people whose ages match and are also in region the selected region. Note You can always replace this "double filter" format with a single eval such as: search('product', 'eval', "#{age} > ${min_age} and #{age} < ${max_age} and ${region} = #{region}", 'eval') |
For more information on using the eval function refer to Get a value using an expression (3 parameters).
Getting Reference Data with the Pulldata Function
The second type of data that you can get from a reference file, or another survey, is reference data. This is data that is "pulled" from its source and added as the answer to a calculate question. It can then be treated like any other answer, and be sent to the server, used in a relevance etc.
There are four versions of the pulldata function with 3, 4, 5 or 6 parameters.
3 params: Get a single value identified using an expression
4 params: Get a single value identified by a specific value in a single filter column
5 params: Get a result for multiple values identified using an expression
6 params: Get a result for multiple values identified by specific value in a single filter column
The Syntax:
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter expression')
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter column', 'filter value')
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter expression', 'index', 'eval')
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter column', 'filter value', 'index', 'filter type')
The most commonly used version is the one with 4 parameters. This is also the standard pulldata version that is used by other data collection tools.
Get a value using a key (4 parameters)
Add a calculate question to your survey and give it a name. For the calculation specify the pulldata function:
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter column', 'filter value')
The source can be the name of a reference file, without its extension or the identifier for another survey.
The column to retrieve is the name of the column in the reference file whose data you want, or the name of the question in the survey that you are looking up.
The filter column is the name of the column / question that identifies the value to retrieve. So if you are looking up the product name using the product code, then this parameter contains the name of the product code column.
The filter value is the value of the filter name that you want. So for the product example if the filter value was set to 'a10' then you would expect to get back the product name for the product with code 'a10'.
Get a value using an expression (3 parameters)
In this approach the 'filter column' and 'filter value' are replaced by an expression. This allows much more flexibility in how the 'column to retrieve' is selected:
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter expression')
When using an expression to filter data you can use the ${question name} syntax to refer to questions in the current survey as usual. However to refer to columns in the reference file or referenced survey use #{column name}.
You can also enclose the whole expression in double quotes. This allows you to use single quotes around text values. For example "#{city} = 'london'"
Data values may need to be "cast" to integer or decimal types. This is because all reference file data is stored as text. For example if you have a filter expression like "#{age} < ${max_age}". Here #{age} is the age value in the reference table and you will need to change your expression to "cast( #{age} as integer ) < ${max_age}". Refer to Converting to a different type for more details.
Warning
In FieldTask4, a pulldata function using an "expression" is not automatically triggered if any of the referenced questions changes their value. FieldTask5 does not have this issue. This means that when using FieldTask4 the pulldata value will not be updated when you were expecting it to be However you can force this behaviour by enclosing the pulldata function within an if() function that references the same questions. The examples below show this approach.
pulldata |
Comment |
|---|---|
if(string-length(${product_code}) > 0, pulldata('products', 'product_name', '#{product_code} = ${product_code} '), '') |
This is the same as the simple product name lookup that was described for the 4 parameter version of pulldata! Note that we use #{product_code} to refer to the value from the product_code column in the reference file. We also refer to the answer to the product code question in the survey using the normal ${} syntax. The pulldata() is enclosed inside an if() function so that FieldTask knows to trigger it when the product_code changes. |
if(string-length(${product_code}) > 0, pulldata('products', 'product_name', '#{product_code} = ${product_code} and #{region} = ${region}'), '') |
Now an example that can't be implemented using the simple 4 parameter version. This example assumes that product codes can be reused in different regions so to get the right product name you also want to filter by region. |
if(string-length(${product_code}) > 0, pulldata('products', 'product_name', "#{product_code} = ${product_code} and #{region} = ${region} and #{year} = '2022' "), '') |
An additional filter by year has been added. Note that because the year is fixed and enclosed in single quotes we have enclosed the whole expression in double quotes. |
Get multiple values (5 and 6 parameters)
The previous examples just returned a single value. If more than one record matches a key just the first will be returned. However you can use repeating groups to show repeating reference data.
The pulldata functions look like this:
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter expression', 'index', 'eval')
pulldata('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter column', 'filter value', 'index', 'filter type')
The first version, 5 parameters, adds an 'index' parameter. The final parameter 'eval' doesn't do anything, it is just there to differentiate this from the standard 4 parameter pulldata function.
The second version, 6 parameters, adds the 'index' parameter and a 'filter type' to the standard 4 parameter version.
Index
The index starts at 1 and allows you to specify which of the multiple matching values you want. So if the index is 3 you will get the answer in the third matching record.
Instead of a number you can use one of the following aggregation functions as the index:
sum - The sum of all the records
mean - The mean or average of the values
min - The minimum value
max - The maximum value
count - The count of the number of matching records
list - All the matching values separated by a space
Note
Where the index is a number it does not have quotation marks.
Filter Type
This is used only with the 6 parameter version and specifies how to filter records. It works in the same way as the filter function in search. In the standard pulldata version this is not needed because the filter type has to be matches since only one record should be found.
contains
startswith
endswith
matches
in
not in
Example usage
type |
name |
repeat_count |
calculation |
comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
calculate |
number_recs |
pulldata('linked_s11_2134', 'complaint_type', 'office', ${office}, 'count', 'matches') |
returns the number of records for the selected office. The second parameter is ignored when using an aggregate function for the index. |
|
begin_repeat |
rpt |
int( ${number_recs} ) |
Creates a repeat group for each matching complaint. Note that the repeat count has to be cast to an integer as calculates have text value by default |
|
note |
type |
pulldata('linked_s11_2134', 'complaint_type', 'office', ${office}, position(..), 'matches') |
The pulldata function is almost the same as before except this time we are getting the value for the record number that corresponds to the position in the repeat. |
|
note |
complaint |
pulldata('linked_s11_2134', 'complaint', 'office', ${office}, position(..), 'matches') |
This time we get the details of the complaint as the value of the note |
|
end_repeat |
rpt |
Support in FieldTask and SmapServer
pulldata version |
FieldTask offline |
FieldTask online |
WebForms offline |
WebForms online |
|---|---|---|---|---|
3 params |
v6.503 |
v6.503 |
v20.09 |
v20.09 |
4 params |
v6.503 |
yes |
yes |
yes |
5 params |
v6.503 |
v6.503 |
v20.09 |
v20.09 |
6 params |
v6.503 |
v6.503 |
v20.09 |
v20.09 |
More Pulldata Examples
You may want to look up the maximum age for a program in a particular region. This example uses the 4 parameter version. In this example we ask what training sector the interviewee is interested in. Then we ask their age. We then do a lookup in the reference file "ref_data.csv" for the maximum allowed age for that sector. Then if the person qualifies we ask them if they want to enroll.
type |
name |
label |
relevant |
calculation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
select_one sectors |
sector |
Which sector? |
||
integer |
age |
What is your age? |
||
calculate |
max_age |
pulldata('ref_data', 'max_age', 'sector', ${sector}) |
||
select_one yes_no |
enroll |
Do you want to enroll? |
${age} <= ${max_age} |
Other examples:
Params |
Calculation |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
3 |
pulldata('cities', 'city_label', "#{country} = 'us' and #{city_label} = 'austin'") |
The csv file 'cities.csv' has a column city_label. The calculation returns the value in the column 'city_label' of the csv file 'cities.csv' where the value in column 'country' is 'us' and in column 'city' is 'austin' |
3 |
if(concat(${country}, ${city_code}) = '', '', pulldata('cities', 'city_label', "#{country} = ${country} and #{city} = ${city_code}")) |
As for the previous example however the search values for country and city_code are the answers to questions. Here the pulldata function has been put inside an if() function that refers to these filter questions. This will make it recalculate when those filter questions change their answer. |
Online Lookup
If you have a network connection when filling in the form then you can replace "pulldata" with "lookup". All other parameters remain the same. The lookup function requires an active connection and does not use local, unsent data. For example:
lookup('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter expression')
lookup('source', 'column to retrieve', 'filter column', 'filter value')
When you have very large amounts of reference data lookup can be more practical. Refer to this article for a discussion on why this is the case.
Local Data
Available with FieldTask version 6.400 and SmapServer version 21.05
Normally when you reference data in other surveys you are looking up data that is stored on the server and has then been copied onto your device. However you may need to complete multiple surveys in a location without an internet connection and while at that remote location you may want to reference data that was entered in another survey but has not been submitted yet.
Surveys have local data searching turned off by default as it could potentially result in significantly longer load times for a survey in cases where the device has been used offline for a significant period of time and there are hundreds of unsent results.
To turn local data searching on with the online editor select the menu File and then Settings. In the settings dialog select the checkbox labelled Lookup local, unsent data on device.
To enable local data searching using the XLSForm editor set a value of "yes" in the column "search_local_data" in the settings worksheet (Survey Settings).
Values from the local unsubmitted data will then be included in data returned from a search() or a pulldata() function. This happens transparently and no further action on your part is required.